skip to main |
skip to sidebar
RSS Feeds
6 Day War weapon, time-line, videos etc
6 Day War weapon, time-line, videos etc
1:15 AM
Posted by Peace Keeper
| SA 321 Super Frelon | |
|---|---|
 | |
| A Super Frelon helicopter n°165 of the 32F Wing flying over Portsmouth | |
| Role | Heavy lift military Transport helicopter |
| Manufacturer | Aérospatiale |
| First flight | 7 December 1962 |
| Introduced | 1966 |
| Primary user | French military |
| Number built | 99 |
| Variants | Avicopter AC313 |
| Sikorsky H-34/S-58 | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Role | Helicopter |
| Manufacturer | Sikorsky Aircraft |
| First flight | 8 March 1954 |
| Introduced | 1954 |
| Status | out of production, still in civilian service |
| Primary users | United States Army United States Navy United States Marines |
| Number built | 2,108 |
| Developed from | H-19 Chickasaw |
| Variants | Westland Wessex |
| Mi-6 | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Mi-6 at Riga, Latvia. | |
| Role | Heavy transport helicopter |
| Manufacturer | Mil Moscow Helicopter Plant |
| First flight | 5 September 1957 |
| Introduction | 1962 |
| Retired | 2002 (Russia CAA) |
| Status | In service with foreign users |
| Primary users | Soviet Air Force Aeroflot |
| Produced | 1960 to 1981 |
| Number built | 925+ |
| Variants | Mil Mi-10 |
| Mi-4 | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Mil Mi-4 at Prague Aviation Museum | |
| Role | Transport helicopter |
| Manufacturer | Mil Moscow Helicopter Plant |
| First flight | 3 June 1952 |
| Introduced | 1953 |
| Status | Retired |
| Primary users | Soviet Air Force Polish Air Force |
| Produced | 1951-1969 |
| Number built | over 4,500 including Z-5s |
| Variants | Harbin Z-5 |
2:25 PM
Posted by Peace Keeper
| Mirage III | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||
| Royal Australian Air Force Mirage IIIO(F) (fighter) from 2 Operational Conversion Unit. | |||||||
| Role | Interceptor aircraft | ||||||
| Manufacturer | Dassault Aviation | ||||||
| First flight | 17 November 1956 | ||||||
| Dimensions |
| ||||||
| Status | Active service | ||||||
| Weight | 15,763 lb (7150 kg) - 32,407 lb (14700 kg) | ||||||
| Speed | Max level speed 'clean' at 39,370 ft (12000 m) 1,453 mph (1,262 kt / 2338 km/h) | ||||||
| Armanent | Cannon: 2 30mm DEFA 552, R.530 R.550 Magic, AS.37 Martel, EU3 450Kg bombs, AN52 nuclear bombs | ||||||
| MiG-21 | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Croatian Air Force MiG-21bis D | |
| Role | Fighter |
| Manufacturer | Mikoyan-Gurevich OKB |
| Designed by | Artem Mikoyan |
| First flight | 14 February 1955 (Ye-2) |
| Introduced | 1959 (MiG-21F) |
| Powerplant | 1 × Tumanskiy R11F-300, 37.27 kN (8,380 lbf) thrust dry, 56.27 kN (12,650 lbf) with afterburner each |
| Maximum speed | 2,125 km/h (1,385 mph), Mach 2.05 |
| Range | 1,580 km (981 miles) |
| Armanent |
|
9:53 AM
Posted by Peace Keeper
| M2 Half Track Car | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Type | Half-track armored personnel carrier |
| Specifications | |
| Weight | 9 metric tons |
| Length | 5.96 m (19 ft 7 in) |
| Width | 2.2 m (7 ft 3 in) |
| Height | 2.26 m (7 ft 5 in) |
| Crew | 2 + 7 passengers |
| | |
| Armor | 6 - 12 mm |
| Primary armament | 0.5 inch M2 Browning machine gun |
| Engine | White 160AX 147 hp (110 kW) |
| Suspension | Wheeled front axle, rear track |
| Operational range | 200 miles (320 km) |
| Speed | 40 mph (64 km/h) |
| Carrier, Personnel Half-track M3 | |
|---|---|
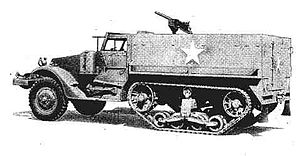 M3 half-track with .30 (7.62 mm) Browning M1919 machinegun | |
| Type | Half-track armored personnel carrier |
| Place of origin | |
| Specifications | |
| Weight | 9.3 t |
| Length | 6.18 m |
| Width | 2.22 m |
| Height | 2.26 m, wheelbase 135.5 in (3,440 mm) |
| Crew | 3 + 10 troops |
| | |
| Primary armament | 1 x 0.5 in (12.7 mm) M2 machine gun |
| Secondary armament | 2 x 0.3 in (7.62 mm) M1919A4 machine guns |
| Engine | White 160AX, 386 cu in (6,330 cc), 6 cylinder, petrol, compression ratio 6.3:1, 147 hp (110 kW) |
| Power/weight | 15.8 hp/tonne |
| Suspension | half track, vertical volute springs; front tread 64.5 in (1,640 mm) to 66.5 in (1,690 mm) |
| Fuel capacity | 60 US gal (230 l) |
| Operational range | 175 mi (282 km) |
| Speed | 45 mph (72 km/h) |
| BTR-40 | |
|---|---|
 Ex-Egyptian or ex-Syrian Israeli-modified BTR-40 at the Yad la-Shiryon Museum, Israel, 2005. | |
| Type | Wheeled Armoured Personnel Carrier Reconnaissance Vehicle |
| Place of origin | |
| Specifications | |
| Weight | 5.3 tonnes |
| Length | 5 m |
| Width | 1.9 m |
| Height | 2.2 m (1.83 m without armament) |
| Crew | 2 + 8 passengers (BTR-40 and BTR-40V) 2 + 6 passengers (BTR-40B) |
| | |
| Armor | 6-8 mm |
| Primary armament | 7.62 SGMB medium machine gun (1,250 rounds (total)) (optional) |
| Secondary armament | 2×7.62 SGMB medium machine gun (1,250 rounds (total)) (optional) |
| Engine | 6-cylinder GAZ-40 80 hp (60 kW) at 3400 rpm |
| Power/weight | 15.1 hp/tonne (11.3 kW/tonne) |
| Suspension | 4x4 wheel, leaf spring |
| Ground clearance | 400 mm |
| Fuel capacity | 122 l |
| Operational range | 430 km (road) 385 km (cross country) |
| Speed | 80 km/h |
| BTR-152 | |
|---|---|
 BTR-152 in Yerevan, Armenia. | |
| Type | Armored personnel carrier |
| Place of origin | |
| Specifications | |
| Weight | 9.91 tonnes |
| Length | 6.55 m 6.83 m for BTR-152V |
| Width | 2.32 m |
| Height | 2.04 m (without the mg) 2.36 m (with the mg) 2.41 m (BTR-152V with the mg) |
| Crew | 2 (+18 passengers) |
| | |
| Armor | welded steel 15 mm front 9 mm sides and rear 10 mm roof 4 mm bottom |
| Primary armament | 7.62mm SGMB light machine gun (1,250 rounds) (12.7 mm DShK 1938/46 heavy machine gun (500 rounds) can be used instead) |
| Secondary armament | 2x7.62mm SGMB light machine guns (1,250-1,750 rounds) on side pintel mounts (optional) |
| Engine | ZIS-123 6 cylinder in-line water-cooled petrol (for variants based on ZiS-151) ZiL-137K 6 cylinder in-line petrol (for variants based on ZiL-157) 110 hp (82 kW) at 3,000 rpm. (for variants based on ZiS-151) 107 hp (80 kW) (for variants based on ZiL-157) |
| Power/weight | 11.1 hp/tonne (8.3 kW/tonne) 10.8 hp/tonne (8.1 kW/tonne) for BTR-152V |
| Suspension | wheeled 6×6 front - 2 leaf springs and hydraulic shock absorbers. rear - equalising type with 2 leaf springs and torsion bars. |
| Ground clearance | 300 mm |
| Fuel capacity | 300 l (79 gal) |
| Operational range | 650 km (404 miles) |
| Speed | 75 km/h[6] 65 km/h for BTR-152V |
| BTR-50 | |
|---|---|
 Israeli-modified ex-Syrian or ex-Egyptian late-production model BTR-50PK APC at the Yad la-Shiryon Museum, Israel. 2005. | |
| Type | Amphibious Tracked Armored Personnel Carrier |
| Place of origin | |
| Specifications | |
| Weight | 14.5 tonnes |
| Length | 7.08 m |
| Width | 3.14 m |
| Height | 2.03 m |
| Crew | 2 (driver and commander) (+20 passengers) |
| | |
| Primary armament | None or 7.62 mm SGMB medium machine gun (BTR-50P) (1,250 rounds) 14.5 mm KPV heavy machine gun (BTR-50PA) 7.62 mm SGMB medium machine gun (BTR-50PK) (1,250 rounds) |
| Secondary armament | none |
| Engine | V-6 6-cylinder 4-stroke in line water cooled diesel 240 hp (179 kW) at 1,800 rpm |
| Power/weight | 16.6 hp/t |
| Suspension | torsion bar |
| Ground clearance | 370 mm |
| Fuel capacity | 400 l |
| Operational range | 400 km |
| Speed | 44 km/h (road) 11 km/h (water) |
| BTR-60 | |
|---|---|
 BTR-60PB | |
| Type | Wheeled Amphibious Armored Personnel Carrier |
| Place of origin | |
| Specifications (BTR-60PB) | |
| Weight | 10.3 tonnes |
| Length | 7.56 m |
| Width | 2.825 m |
| Height | 2.31 m |
| Crew | 3 + 8 passengers |
| | |
| Armor | Welded steel 7 mm at 86° hull upper front 9 mm at 47° hull lower front 7 mm hull sides 5 mm hull upper rear 7 mm hull lower rear 5 mm hull floor 7 mm hull roof 10 mm turret front 7 mm turret sides 7 mm turret sear 7 mm turret roof |
| Primary armament | 14.5mm KPVT heavy machine gun (500 rounds) |
| Secondary armament | 7.62 mm PKT tank coaxial machine gun (3,000 rounds) |
| Engine | 2×GAZ-40P 6-cylinder gasoline 90 hp (67 kW) each 180 hp (134 kW) (combined) |
| Power/weight | 18.4 hp/tonne (13.7 kW/tonne) |
| Suspension | wheeled 8×8 |
| Ground clearance | 475 mm |
| Fuel capacity | 290 l |
| Operational range | 500 km |
| Speed | 80 km/h on road 10 km/h on water |
12:44 PM
Posted by Peace Keeper

| M48 Patton | |
|---|---|
 M48A1 medium tank | |
| Type | Medium Tank |
| Place of origin | |
| Specifications | |
| Weight | M48: 49.6 tons (45 tonnes) combat ready |
| Length | 30.22' (9.3 m) |
| Width | 11.86' (3.65 m) |
| Height | 10.07' (3.1 m) |
| Crew | 4 (commander, gunner, loader, driver) |
| | |
| Armor | 120 mm (4.89") |
| Primary armament | 90 mm gun T54; M48A3 90mm gun M41; M48A5 and later variants: 105 mm M68 gun |
| Secondary armament | .50 in (12.7 mm) M2 Browning machine gun .30 in (7.62 mm) M73 Machine gun |
| Engine | Continental AVDS-1790-5B V12, air-cooled Twin-turbo gasoline engine (early M48s) 810 hp (604 kW) Continental AVDS-1790-2 V12, air cooled Twin-turbo diesel engine |
| Power/weight | 15.1 hp/ton (16.6/tonne) |
| Transmission | General Motors CD-850-4A or -4B, 2 ranges forward, 1 reverse |
| Suspension | Torsion bar suspension |
| Fuel capacity | 200 gals (757 litres) |
| Operational range | 287 miles (463 km) |
| Speed | 30 mph (48 km/h)(M48A5) |
| Centurion | |
|---|---|
 Centurion Mk3 | |
| Type | Main battle tank |
| Place of origin | |
| Specifications | |
| Weight | 51 long tons (52 t) |
| Length | 25 ft (7.6 m) |
| Width | 11 feet 1 inch (3.38 m) |
| Height | 9 feet 10.5 inches (3.010 m) |
| Crew | 4 (commander, gunner, loader, driver) |
| | |
| Armour | 6 in (150 mm) |
| Primary armament | 105 mm L7 rifled gun 17 pdr 20 pdr |
| Secondary armament | .30 cal Browning machine gun |
| Engine | Rolls Royce Meteor 650 hp (480 kW) |
| Power/weight | 13 hp/tonne |
| Suspension | Horstmann suspension |
| Operational range | 280 miles (450 km) |
| Speed | 21 mph (34 km/h) |
| AMX 13 | |
|---|---|
 AMX-13 on display | |
| Type | Light tank |
| Place of origin | |
| Specifications | |
| Weight | 13.7 t (30,000 lb) empty 14.5 t (32,000 lb) combat |
| Length | 4.88 m (16 ft 0 in) hull 6.36 m (20 ft 10 in) with gun |
| Width | 2.51 m (8 ft 3 in) |
| Height | 2.35 m (7 ft 9 in) |
| Crew | 3 (Commander, gunner and driver) |
| | |
| Armour | 10mm (.39 in) minimum 40 mm (1.57 in) maximum |
| Primary armament | 75 mm (or 90 mm or 105 mm) with 32 Rounds |
| Secondary armament | 7.5 mm (or 7.62 mm) coaxial MG with 3,600 Rounds, 7.62 mm AA MG (optional), 2×2 smoke grenade dischargers |
| Engine | SOFAM Model 8Gxb 8-cyl. water-cooled petrol 250 hp (190 kW) |
| Power/weight | 15 hp/tonne |
| Suspension | Torsion bar suspension |
| Operational range | 400 km (250 mi) |
| Speed | 60 km/h (37 mph) |
| T-34 | |
|---|---|
 T-34-85 at Musée des Blindés | |
| Type | Medium tank |
| Place of origin | |
| Specifications (T-34 Model 1941) | |
| Weight | 26.5 tonnes (29.2 ST; 26.1 LT) |
| Length | 6.68 m (21 ft 11 in) |
| Width | 3.00 m (9 ft 10 in) |
| Height | 2.45 m (8 ft 0 in) |
| Crew | 4 |
| | |
| Armor | (typical)[1] upper front 45 mm (1,8")/60°, hull side 45 mm (1.8")/40°(upper part), rear 40 mm, top 20 mm, bottom 15 mm; turret front 60 mm (2.4"), sides up to 63 mm/2.5"/30°, rear 40 mm, top 16 mm |
| Primary armament | 76.2 mm (3.00 in) F-34 tank gun |
| Secondary armament | 2 × 7.62 mm (0.308 in) DT machine guns |
| Engine | 12-cyl. diesel model V-2 500 hp (370 kW) |
| Power/weight | 17.5 hp/tonne |
| Suspension | Christie |
| Operational range | 400 km (250 mi) |
| Speed | 53 km/h (33 mph) |
| T-54/55 | |
|---|---|
 Polish T-55A, Poznań Citadel Museum of Arms (front · rear · detail) | |
| Type | Main battle tank |
| Place of origin | |
| Service history | |
| In service | 1950–present |
| Specifications (T-55) | |
| Weight | 39.7 tonnes |
| Length | 6.45 m |
| Width | 3.37 m |
| Height | 2.40 m |
| Crew | 4 |
| | |
| Armour | 203 mm turret, 99 mm hull, LOS = ~200 mm |
| Primary armament | D-10T 100 mm rifled gun |
| Secondary armament | 2×7.62 mm SGMT machine gun, (12.7 mm DShK heavy machine gun) |
| Engine | Model V-55 12-cyl. 38.88-l diesel 581 hp (433 kW) |
| Power/weight | 14.6 hp/tonne |
| Suspension | Torsion bar |
| Ground clearance | 0.425 m |
| Fuel capacity | 961 l (254 gal) |
| Operational range | 501 km (311 mi), 600 km (373 mi) with extra tanks |
| Speed | 55 km/h (34 mph) |
| PT-76 | |
|---|---|
 PT-76 on display near the Museum of the Great Patriotic War, Kiev | |
| Type | Amphibious Light Tank |
| Place of origin | |
| Specifications (PT-76 model 1) | |
| Weight | 14.6 tonnes |
| Length | 6.91 m (hull) |
| Width | 3.15 m |
| Height | 2.325 m |
| Crew | 3 (driver, commander, loader) |
| | |
| Armour | 20 mm |
| Primary armament | 76,2 mm D-56T rifled tank gun (40 rds.) |
| Secondary armament | 7.62 mm SGMT coax machine gun (1,000 rds.) |
| Engine | 6-cyl. diesel 240 hp (179 kW) |
| Power/weight | 16.4 hp/tonne |
| Suspension | torsion-bar |
| Ground clearance | 370 mm |
| Fuel capacity | 250 l |
| Operational range | 370–400 km, 480–510 km with external fuel |
| Speed | 44 km/h (27 mph), 10.2 km/h (6.3 mph) swimming |
| Panzerkampfwagen IV | |
|---|---|
 A Panzer IV Ausf G. in desert colors, bearing the palm tree insignia of the 15th Panzer Division of the Afrika Korps. | |
| Type | Medium tank |
| Place of origin | |
| Specifications (Pz IV Ausf H, 1943 [2]) | |
| Weight | 25.0 tonnes (27.6 ST; 24.6 LT) |
| Length | 7.02 m (23 ft 0 in) |
| Width | 2.88 m (9 ft 5 in) |
| Height | 2.68 m (8 ft 10 in) |
| Crew | 5 (commander, gunner, loader, driver, radio operator/bow machine-gunner) |
| | |
| Armor | 10–80 mm (0.39–3.1 in) |
| Primary armament | 7.5 cm (2.95 in) KwK 40 L/48 main gun (87 rds.) |
| Secondary armament | 2-3 × 7.92-mm Maschinengewehr 34 |
| Engine | 12-cylinder Maybach HL 120 TRM 300 PS (296 hp, 220 kW) |
| Power/weight | 12 PS/t |
| Transmission | 6 forward and 1 reverse ratios |
| Suspension | Leaf spring |
| Fuel capacity | 470 l (120 US gal) |
| Operational range | 200 km (120 mi) |
| Speed | 42 km/h (26 mph) road, 16 km/h (9.9 mph) off road |
| M47 Patton | |
|---|---|
 M47 Patton on display | |
| Type | Medium Tank[1] |
| Place of origin | |
| Specifications | |
| Weight | 46 tonnes (50.7 short tons) combat ready |
| Length | 27 ft 11 in (8.51 m) |
| Width | 11 ft 6.25 in (3.51 m) |
| Height | 11 ft (3.35 m) |
| Crew | 5 (commander, gunner, loader, driver, assistant driver) |
| | |
| Armor | 4 in (100 mm) |
| Primary armament | 90 mm gun M36 71 rounds |
| Secondary armament | 0.5 in (12.7 mm) M2 machine gun 2 × 7.62 mm machine gun |
| Engine | Continental AVDS-1790-5B V12, air-cooled, Twin-turbo gasoline engine 810 hp (600 kW) |
| Power/weight | 17.6 hp/tonne |
| Transmission | General Motors CD-850-4, 2 ranges forward, 1 reverse |
| Suspension | Torsion bar |
| Fuel capacity | 231.94 gallons (878 liters) |
| Operational range | 81 mi (130 km) |
| Speed | 30 mph (48 km/h) |
| M48 Patton | |
|---|---|
 M48A1 medium tank | |
| Type | Medium Tank |
| Place of origin | |
| Specifications | |
| Weight | M48: 49.6 tons (45 tonnes) combat ready |
| Length | 30.22' (9.3 m) |
| Width | 11.86' (3.65 m) |
| Height | 10.07' (3.1 m) |
| Crew | 4 (commander, gunner, loader, driver) |
| | |
| Armor | 120 mm (4.89") |
| Primary armament | 90 mm gun T54; M48A3 90mm gun M41; M48A5 and later variants: 105 mm M68 gun |
| Secondary armament | .50 in (12.7 mm) M2 Browning machine gun .30 in (7.62 mm) M73 Machine gun |
| Engine | Continental AVDS-1790-5B V12, air-cooled Twin-turbo gasoline engine (early M48s) 810 hp (604 kW) Continental AVDS-1790-2 V12, air cooled Twin-turbo diesel engine |
| Power/weight | 15.1 hp/ton (16.6/tonne) |
| Transmission | General Motors CD-850-4A or -4B, 2 ranges forward, 1 reverse |
| Suspension | Torsion bar suspension |
| Fuel capacity | 200 gals (757 litres) |
| Operational range | 287 miles (463 km) |
| Speed | 30 mph (48 km/h)(M48A5) |
6:24 AM
Posted by Peace Keeper
As a result of the war, a wave of Palestinians was displaced. An estimated 300,000 Palestinians left the West Bank and Gaza, most of whom settled in Jordan.
In his book Righteous Victims, Israeli "New Historian" Benny Morris writes:
In three villages southwest of Jerusalem and at Qalqilya, houses were destroyed "not in battle, but as punishment ... and in order to chase away the inhabitants ... ---contrary to government...policy," Dayan wrote in his memoirs. In Qalqilya, about a third of the homes were razed and about 12,000 inhabitants were evicted, though many then camped out in the environs. The evictees in both areas were allowed to stay and later were given cement and tools by the Israeli authorities to rebuild at least some of their dwellings. But many thousands of other Palestinians now took to the roads. Perhaps as many as seventy thousand, mostly from the Jericho area, fled during the fighting; tens of thousands more left over the following months. Altogether, about one-quarter of the population of the West Bank, about 200-250,000 people, went into exile. ... They simply walked to the Jordan River crossings and made their way on foot to the East Bank. It is unclear how many were intimidated or forced out by the Israeli troops and how many left voluntarily, in panic and fear. There is some evidence of IDF soldiers going around with loudspeakers ordering West Bankers to leave their homes and cross the Jordan. Some left because they had relatives or sources of livelihood on the East Bank and feared being permanently cut off. Thousands of Arabs were taken by bus from East Jerusalem to the Allenby bridge, though there is no evidence of coercion. The free Israeli-organized transportation, which began on June 11, 1967, went on for about a month. At the bridge they had to sign a document stating that they were leaving of their own free will. Perhaps as many as seventy thousand people emigrated from the Gaza Strip to Egypt and elsewhere in the Arab world. On July 2 the Israeli government announced that it would allow the return of those 1967 refugees who desired to do so, but no later than August 10, later extended to September 13. The Jordanian authorities probably pressured many of the refugees, who constituted an enormous burden, to sign up to return. In practice only 14,000 of the 120,000 who applied were actually allowed by Israel back into the West Bank by the beginning of September. After that, only a trickle of "special cases" were allowed back, perhaps 3,000 in all.(328-9)
In addition, between 80,000 and 110,000 Syrians fled the Golan Heights, of which about 20,000 were from the city of Quneitra. According to recent research by an Israeli daily Haaretz, much of the Syrian population was expelled from the territory by the Israeli army.
With the loss of Arab lands, the minority Jews living in the Arab world immediately faced persecution and expulsion, following the Israeli victory. According to historian Michael B. Oren,
mobs attacked Jewish neighborhoods in Egypt, Yemen, Lebanon, Tunisia, and Morocco, burning synagogues and assaulting residents. A pogrom in Tripoli, Libya, left 18 Jews dead and 25 injured; the survivors were herded into detention centers. Of Egypt's 4,000 Jews, 800 were arrested, including the chief rabbis of both Cairo and Alexandria, and their property sequestered by the government. The ancient communities of Damascus and Baghdad were placed under house arrest, their leaders imprisoned and fined. A total of 7,000 Jews were expelled, many with merely a satchel.
5:45 AM
Posted by Peace Keeper
| June 18, 1953 | Revolution in Egypt. Young officers including Gemal Abdel Nasser overthrow monarchy and proclaim goal of modernization and undoing the shame of 1948. |
| Oct. 29, 1956 | Suez Campaign. In retaliation for a series of escalating border raids as well as the closure of the straits of Tiran and Suez canal to Israeli shipping, and to prevent Egyptian use of newly acquired Soviet arms in a war, Israel invades the Sinai peninsula and occupies it for several months, with French and British collaboration. French and British were interested in reversing the nationalization of the canal. Israel withdraws after a UN peace keeping force is placed in Sinai, and US guarantees right of passage for Israeli shipping through the Straits of Tiran. Suez Canal reopened March 23, 1957. |
| 1957 | Probable start of construction of Israel nuclear breeder reactor using French technology. The French later tried to stop the program, but backed down when Israeli FM Peres said Israel would make the deal public. Reactor was discovered by the US in U-2 flights in 1960 or 1961. |
| 1957 | U.S. committed in an aide de memoire (memorandum) to guarantee freedom of passage in the Suez canal, signed February 11. A later memorandum of February 23 answered questions and clarified Israeli doubts, making it clear that US would allow use of force to keep the straits open. However, the US government later claimed that it had no knowledge of such commitments and that the memorandum was "lost." |
| Nov 18, 1959 | Israel abandons earlier Jordan river diversion scheme, begins work on the National Water Carrier Project, to divert the waters of the River Jordan from the Sea of Galilee to the Negev, taking its share of Jordan water in accordance with Johnston plan. |
| 1959 | Fatah founded. In the summer of 1959, according to a detailed account by Thomas Kiernan, Yasser Arafat, Khalil al Wazir, Saad Khalef, Faruq Qadumi, Zuhair al Alami, Kamal Adwan, Muhamed Yussef an-Najar and others found the Fatah organization in Kuwait, with the aim of destroying Israel. The name means victory or conquest.As "conquest" does not sound politically correct, they note that they can reverse the name to be Harakat Tahrir Filastin, Palestine Liberation Movement. Various dates and soon renamed "Fatah" (Conquest or "Victory"). The organization was to be modeled on the Algerian FLN. (from Kiernan, Thomas, Arafat, Norton, 1976 pp 214-218). Various other dates as early as 1957 are given in other sources, and may refer to informal meetings held by the Palestinian expatriate group surounding Arafat.Fatah was formally founded in 1964. |
| Oct. 23, 1958 | Soviet loan to Egypt to finance Aswan Dam. |
| Nov 18, 1959 | Israel abandons earlier Jordan river diversion scheme, begins work on the National Water Carrier Project, to divert the waters of the River Jordan from the Sea of Galilee to the Negev, taking its share of Jordan water in accordance with Johnston plan. |
| Jan 13-17 1964 | First Arab summit at Cairo (the Egyptians count this as the third Arab Summit) (ie. heads of State, instigated by Nasser), prompted by Israel’s national water carrier project and Palestinian agitation against it. Arabs declare their intentions of stopping the Israeli diversion scheme, which is in accordance with the Johnson plan, and decided on establishment of the PLO. A Unified Arab Command under Egyptian supervision was created. This summit and the one that followed in September caused considerable alarm in Israel, and is cited by Avi Shlaim (The Iron Wall) as the actual beginning of the 6 day war. |
| May, 1964 | PLO (Palestine Liberation Organization)founded with the aim of destroying Israel. The Palestinian National Charter (1968) officially called for liquidation of Israel. PLO was founded by Egypt to divert Palestinian energies from the nascent Fatah movement of Yasser Arafat, which had become anti-Nasserist. |
| June 5, 1964 | Israel begins pumping water from the Sea of Galilee for the Israel National Water Carrier. Israel agreed to take only its share of water allotted under the Johnston plan, with the tacit agreement of Jordan. |
| Sept 13, 1964 | Second Arab Summit at Alexandria decides on diversion of the headwaters of the Jordan as well as strengthening regional Arab armies. Arabs declare the aim of destroying Israel. Israel addressed two notes to the UN Security Council, concerning the alarming nature of the summit resolutions to destroy Israel. |
| Jan. 2, 1965 | Al Fatah carries out first sabotage in Israel, against the Israel National Water Carrier. Fatah carried out about 122 raids between Jan 1965 and June 1967, later boasting that they had dragged the Arab states into war. Most of these raids were abortive |
| Jan. 1965 | Syrians capture Israeli agent Eli Cohen, cutting off an important source of intelligence about Syrian deployment, particularly in the Golan. Cohen was executed in May. |
| 1965 | Syrian water diversion project begins. Syrians fire on Israeli demilitarized zones, often in response to Israeli provocations. This gives Israel the excuse to bombard earth moving equipment of the diversion project. |
| Sept. 18. 1965 | Third Arab Summit at Casablanca. Conference draws up staged plan for combating Israel, first building up armed forces of Jordan, Syria and Lebanon over 2.5-3 yrs & refraining from war with Israel; then proceeding to war. |
| Nov 13, 1965 | After Syria fires on Israeli patrol, IAF bombards Syrian diversion project in retaliation. Four Israelis killed, heavier losses for Syrians. |
| Feb. 23, 1966 | Baathist extremist coup in Syria by Shazli Al Jadid and Hafez El Assad, followed by increased PLO activity against Israel. Regime policy: "The Palestine question [is] the main axis of our domestic, Arab and international policies... The liberation battle can only be waged by progressive Arab forces through a popular war of liberation, which history has proved is the only course for victory against all aggressive forces.... it will remain the final way for the liberation of the entire Arab homeland and for its comprehensive socialist popular unification. |
| May 25, 1966 | USSR claims falsely that it has uncovered a Zionist plot to attack Syria. |
| July 7, 1966 | IAF attacks Syrian diversionary scheme after Syrian shelling of Israel, and downs a MiG 21. The diversion scheme is abandoned. |
| Aug 15, 1966 | Israeli patrol boat run ashore in DMZ on Eastern shore of lake Galilee is attacked by Syrian air force and artillery. Israel air force downs two MiGs, but the boat must be salvaged at night due to persistent artillery fire. |
| Nov 9, 1966 | Egypt and Syria sign defense treaty. This date is also given as Nov. 4. A secret codicil promised that Egypt would attack Israel in the south if Israel attacked Syria. |
| Nov 10, 1966 | Three Israeli soldiers are killed by a land mine on an Israeli patrol road near the the border, south of Hebron. King Hussein sends an apology via US ambassador Walworth Barbour, but Barbour fails to deliver the apology. |
| Nov 13, 1966 | Samu' raid: Israeli troops retaliate for the November 10 killing of 3 Israeli soldiers by a mine planted on a patrol road. The attack unexpectedly runs into a column of Jordan Legion soldiers, kills 15 Jordanian soldiers and 3 civilians, & dynamite 125 houses in as Samu according to UN or about 40 according to Israelis.near Hebron; in response to the Israel is censured by SCR228 (25 Nov 66), but there is no military response from Amman. This leads to recriminations in the Israeli government, which had intended a smaller scale raid, and Palestinian anger and clashes with Jordanian security forces throughout West Bank, especially in Nablus where the army had to intervene. The PLO gains support. |
| Dec 14, 1966 | Egyptian Marshal Hakim Amer cables Nasser from Pakistan, recommending closing the straits of Tiran to Israeli shipping and dismissing the UNEF force from Gaza. |
| Jan -March 1967 | Over 270 border "incidents" cause rising concern in Israel. March 3 - Landmine injures tractorist in Kibbutz Shamir. March 12, explosion on train tracks near Kibbutz Lahav. March 26, 2 Palestinians killed trying to demolish a water pump near Arad. |
| April 7, 1967 | Israelis respond to intensive Syrian shelling of DMZ and and Israeli villages and kibbutzim with IAF raid. An air battle involving about 130 aircraft developed. Israelis down 6 MiG 21 fighters, 2 over the Golan and 4 over Damascus. |
| May 11, 1967 | Israeli PM Eshkol states, "In view of the 14 incidents in the past month alone it is possible that we will have to adopt measures no less drastic than those of April 7." UPI circulated a rumor (May 12) that Israel was trying to topple the Syrian regime. The incidents included shelling, terror attacks and attempted infiltration of a Syrian agent to blow up locations in Jerusalem. |
| May 12, 1967 | Remarks by Yitzhak Rabin interpreted as provocative against Syria. Rabin is rebuked by Eshkol. |
| May 13, 1967 | Soviets inform Anwar Sadat in Moscow that Israel is massing 10-12 brigades in preparation for an attack on Syria, supposedly to take place May 17. The information is false, as were several similar previous Soviet warnings. |
| May 14, 1967 | First reports of Egyptian troop movements into Sinai. |
| May 16, 1967 | Radio Cairo broadcast stated: "The existence of Israel has continued too long. We welcome the Israeli aggression. We welcome the battle we have long awaited. The peak hour has come. The battle has come in which we shall destroy Israel." |
| May 18, 1967 | Egyptian President Gamal Abdel Nasser orders the United Nations Emergency Force to leave Sinai. |
| May 21, 1967 | Ben-Gurion summons Israeli Chief of Staff Rabin and accuses him of precipitating the crisis and dragging Israel into a dangerous war. On the following day, Rabin, under tremendous pressure, is incapacitated temporarily by nicotine poisoning, massive fatigue or a nervous breakdown. |
| May 23, 1967 | Egyptian President Gamal Abdel Nasser closes the straits of Tiran to Israeli shipping. Egypt moves six divisions, about 130,000 soldiers, into Sinai. Negotiations with US to reopen the Straits of Tiran fail. |
| May 26, 1967 | Speech by Gamal Nasser to Arab Trade Unionists - - Nasser claimed that Egypt was only looking for the right movement and the proper excuse to fight for the Palestinian cause. |
| May 26, 1967 | President Johnson reluctantly agrees to see Abba Eban. Tells him he is powerless to act to open straits of Tiran and requires more time (about two weeks) to assemble UN support for a regatta to open the straits. Warns Israel against unilateral action. Subsequent UN debate proves fruitless. |
| May 27, 1967 | Nasser cancels a planned Egyptian attack on Israel (Operation fajr - Dawn), planned for following day, after it became obvious that the Israelis knew about the plan. |
| May 28, 1967 | Israeli Levi Eshkol broadcasts a hesitant, stammering speech, further exacerbating pressure on him to make way for other leaders. Later it is claimed that the stammering was due to problems in reading the manuscript. |
| May 29, 1967 | Speech by Gamal Nasser to Egyptian National Assembly Members - Nasser explicitly threatened to destroy Israel: "...God will surely help and urge us to restore the situation to what it was in 1948....But now that the time has come - and I have already said in the past that we will decide the time and place and not allow them to decide - we must be ready for triumph and not for a recurrence of the 1948 comedies. " |
| May 30, 1967 | Jordan signs a defense pact with Egypt, allows Egyptian command of Jordan Legion. |
| May 31, 1967 | President Abdur Rahman Aref of Iraq stated "The existence of Israel is an error which must be rectified. This is our opportunity to wipe out the ignominy which has been with us since 1948. Our goal is clear - to wipe Israel off the map. |
| Jun 2, 1967 | Moshe Dayan joins Israeli cabinet as Minister of Defense. Unity gov't formed. Reservists released for furlough before outbreak of the war. |
| Day 1 | Egyptian Front | Jordanian Front | Syrian Front | |||
| June 5 | 7:46 | First wave of Israeli air attacks in Operation Focus; hits Egypt. | 9:45 | Jordanian bombardment of Jerusalem & Central Israel. Iraqi and Jordanian aircraft try to bomb Tel Aviv & other targets. | ||
| 8:15 | Southern District Commander Yehushua Gavish gives attack order. Tal's division crosses southern Gaza into Rafiah; Jordanian radar at Ajlun detects the Israeli attack and warns Egyptians, but the Egyptians do not get the transmission. | 12:00 | Israeli bombing of airfields in Mafraq and Amman. Jordanians capture UNO HQ in Jerusalem. | 12:00 | Syrian aircraft attack targets in Haifa | |
| 10:15 | Seventh Brigade in Khan Yunis. | 12:25 | Israel bombs Iraq airbase H-3 | |||
| 16:00 | IAF attacks Cairo International Airport, destroying combat aircraft hidden under the wings of civilian airliners.* | 13:00 | Jerusalem brigade captures UN governor's HQ in Jerusalem. | |||
| 17:00 | Seventh brigade armor in El Arish; mopping up in Rafiah | 15:00 | 45th Israel armored brigade crosses border near Ta'anach | 13:00 | IAF aircraft attack Syrian airbases, destroy most of the Syrian air force. | |
| 18:30 | Yoffe's division at Bir al lachfan junction. | 15:30 | Israel conquers Tsur Baher and Pa'amon fortified position. | |||
| 22:00 | IN ships in Alexandria & Port Said. | 17:00 | Jordanian artillery shell Tel Aviv | |||
| 19:30 | Israel takes "Radar" and Sheikh Abd al-Aziz positions. | 1840 | Syrian artillery bombards Rosh Pina | |||
| Day 2 | Egyptian Front | Jordanian Front | Syrian Front | |||
| June 6 | 6:00 | Sharon's division completes conquest of Umm el Katef, Afu Ageila | 3:00 | Latrun Police fort captured by 55th brigade & 4th armored brigade; 10th brigade cuts off Jerusalem-Ramallah road | 05:47 | Syrian artillery barrage on Israeli border communities and attempt to advance to Tel Dan, Dan and Ashmora. |
| 12:00 | Conquest of Bir al Lahfan completed. Tal and Yoffe link up. | 05:30 | 45th Brigade enters Jenin. | |||
| 13:00 | Conquest of Gaza complete | 06:00 | Counterattack of Jordan Legion 40th brigade in Dotan valley. | |||
| 16:00 | Ras el Naqeb conquered | 06:15 | Conquest of "armor hill" ("givat hatahmoshet") in Jerusalem. | |||
| 18:30 | Jebel Libni junction conquered | 08:00 | North East Jerusalem conquered | |||
| 20:00 | General retreat ordered for Egyptian army. | 11:00 | 37th brig. captures Talpit | |||
| 11:45 | Capture of "Givat Hamivtar" | |||||
| 13:00 | Jenin Surrenders | |||||
| 17:00 | End of Dotan valley battler | |||||
| 17:20 | Qalqiliya conquered by IDF | |||||
| 18:00 | Abu Tor conquered by IDF | |||||
| 19:30 | Conquest of Ramallah | |||||
| 24:00 | General retreat from West Bank (Judea & Samaria) ordered for Jordan Legion. | |||||
| Day 3 | Egyptian Front | Jordanian Front | Syrian Front | |||
| June 7 | 0900 | Bir al-Hasna conquered | 02:00 | Zabbida-Aqaba conquered conquered. | Syrian artillery bombardments continue all along the northern border with Golan. | |
| 11:00 | Al Qazima conquered. | 10:00 | Old city of Jerusalem conquered. | |||
| 12:14 | Israel Navy at Sharm el Sheikh | 11:00 | Tul Karm conquered | |||
| 11:15 | Nablus (Shechem) conquered. | |||||
| 12:15 | Final general retreat order for Jordanian forces. | |||||
| 14:30 | Bir Gafgafa conquered | 14:25 | Mar Elias monastery conquered | |||
| 18:00 | Mitleh pass closed | 18:00 | Gush Etzion conquered by Israel. | |||
| 19:40 | Nasser turns down UN Security Council cease fire initiative. Israeli fourth division preventing Egyptian retreat at Mitleh and Jiddi passes | 19:30 | Jericho conquered by Israel. | |||
| Day 4 | Egyptian Front | Jordanian Front | Syrian Front | |||
| June 8 | 03:00 | 3d Eg. armored brigade attacks Tal's vanguard west of Bir Gafgafa. | 06:30 | IDF conquers Hebron. | Syrian artillery bombardments continue all along the northern border with Golan. | |
| 5:55 | Israel reconnaissance flight spots ship off Gaza coast, later identified as USS Liberty, and marked on Israeli situation map. Liberty had not received cables ordering it to withdraw 100 miles from the coast. | 08:00 | Link up of central and southern command forces at Dahirieh (west of Hebron). | IAF attacks Syrian defenses in preparation for operation Hammer, which is then cancelled. | ||
| 06:00 | Kuntilah conquered. | 13:00 | IDF destroys Jordan river bridges. | |||
| 9:00 | Israeli pilots spot Liberty 30 km north of El Arish. Rabin summons US Naval attache and warns him to identify or remove U.S. ships from battle zone. Israeli requests for naval liaison were repeatedly refused by US. | |||||
| 10:00 | Israeli battle with Egyptian reserve at Kantara approaches. Jiddi pass conquered by Israelis. | |||||
| 11:00 | Israeli duty officer goes off shift, removes Liberty marker. | |||||
| 11:24 | Explosion of ammunition dumps at El-Arish mistakenly attributed by Israelis to naval attack. Rabin repeats order to sink any unidentified ships. | |||||
| 01:41 | Liberty spotted, but not identified, by Israeli torpedo boats, who request air assistance. Israeli air reconnaissance fails to identify the ship. | |||||
| 01:57 | 2 Israeli Mirages strafe the Liberty. A squad of Mysteres dropped napalm on the ship. Before renewing the attack, Israelis identify Latin alphabet lettering, showing the ship was not Arab, and break off attack. | |||||
| | Torpedo ship squadron pagoda, ordered to hold back, nonetheless arrives on the scene of the USS Liberty battle and fires five torpedoes at the ship after US personnel fire at the torpedo boats. | |||||
| 15:30 | Egypt accepts cease fire (9:30 PM N.Y. time) | |||||
| 16:00 | End of Kalat a-nahal battle. | |||||
| 18:00 | Kantara conquered | |||||
| Day 5 | Egyptian Front | Jordanian Front | Syrian Front | |||
| June 9 | 01:00 | Yoffe's advance armor reaches Suez Canal | 07:20 | After intercepted message from Nasser indicates Arab forces are near collapse, Dayan reverses his stand and the decision of the cabinet, and orders attack on the Golan Heights. Initially a limited plan called "Hammer." | ||
| 11:30 | 8th brig. begins advance on Syrian lines in North Golan | |||||
| 12:35 | IDF conquers Tel Hallal | |||||
| 17:00 | IDF conquers Tel Azaziat | |||||
| 18:20 | IDF takes Tal Fahr bunkers after bloody battle. | |||||
| 18:30 | Nasser, in televised speech, blames the United States for the loss and insists that the US helped Israel. He threatens "The Sixth Fleet runs on Arab Petroleum." Nasser announces resignation. Speech is followed by anti-aircraft fire and a huge "spontaneous demonstration" that causes him to retract the resignation. | 18:30 | IDF takes Zaura-Kala compound. | |||
| 20:00 | IDF takes Rouya | |||||
| Day 6 | Egyptian Front | Jordanian Front | Syrian Front | |||
| June 10 | 0:400 | IDF conquers Jalabina fortifications. | ||||
| 08:30 | Syrians announce falsely that Kuneitra has fallen, in order to pressure for a cease fire. | |||||
| 14:30 | Kuneitra falls to IDF (12:30 according to Michael Oren, 6 Days of War) | |||||
| 15:00 | Dayan meets Odd Bull and agrees to cease fire by 18:00 hrs. | |||||
| 18:15 | Mas'ada falls. | |||||
| Day | Egyptian Front | Jordanian Front | Syrian Front | |||
| June 12 | Hermon and Majdal Chams claimed for Israel. | |||||